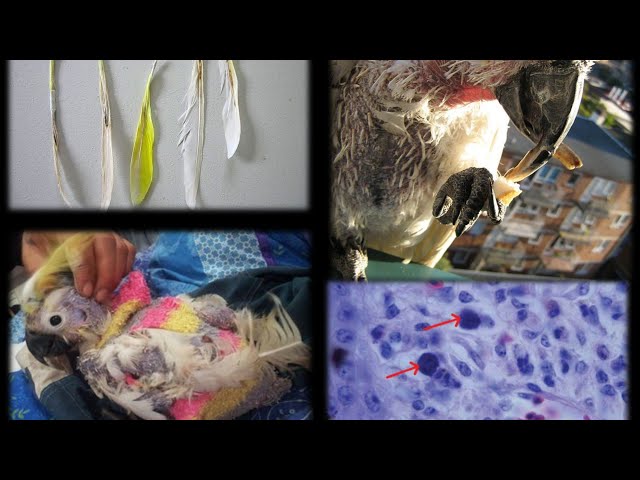
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is a viral disease that affects parrots and other psittacine birds. It is caused by a circovirus, which is a type of virus that has a circular DNA genome. PBFD can cause a variety of symptoms, including feather loss, beak deformities, and immunosuppression. The virus is highly contagious and can be spread through contact with infected birds or their feces. There is no cure for PBFD, but treatment can help to manage the symptoms and improve the bird’s quality of life.
PBFD is a serious disease that can have a devastating impact on affected birds. Feather loss can make it difficult for birds to fly and thermoregulate, and beak deformities can make it difficult for them to eat and drink. Immunosuppression can also make birds more susceptible to other infections. PBFD is a major concern for bird owners and breeders, and there is a great deal of research being conducted to develop new treatments and vaccines.
Importance of PBFD
- PBFD is a highly contagious disease that can affect a wide range of psittacine birds.
- There is no cure for PBFD, but treatment can help to manage the symptoms and improve the bird’s quality of life.
- PBFD can have a devastating impact on affected birds, causing feather loss, beak deformities, and immunosuppression.
- PBFD is a major concern for bird owners and breeders, and there is a great deal of research being conducted to develop new treatments and vaccines.
Psittacine Beak and Feather Disease
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is a serious viral disease that affects parrots and other psittacine birds. It is caused by a circovirus, which is a type of virus that has a circular DNA genome. PBFD can cause a variety of symptoms, including feather loss, beak deformities, and immunosuppression. The virus is highly contagious and can be spread through contact with infected birds or their feces. There is no cure for PBFD, but treatment can help to manage the symptoms and improve the bird’s quality of life.
- Cause: Circovirus
- Symptoms: Feather loss, beak deformities, immunosuppression
- Transmission: Contact with infected birds or their feces
- Diagnosis: Physical exam, blood test, PCR test
- Treatment: Supportive care, antiviral medication
- Prevention: Vaccination, quarantine of new birds
PBFD is a devastating disease that can have a significant impact on the health and well-being of affected birds. Feather loss can make it difficult for birds to fly and thermoregulate, and beak deformities can make it difficult for them to eat and drink. Immunosuppression can also make birds more susceptible to other infections. PBFD is a major concern for bird owners and breeders, and there is a great deal of research being conducted to develop new treatments and vaccines.
In conclusion, the key aspects of psittacine beak and feather disease that we have discussed include its cause, symptoms, transmission, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Understanding these aspects is essential for bird owners and breeders in order to prevent and control this disease.
Cause
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is caused by a circovirus, which is a type of virus that has a circular DNA genome. Circoviruses are highly contagious and can be spread through contact with infected birds or their feces. They are very hardy and can survive in the environment for long periods of time.
- Transmission: Circoviruses are spread through contact with infected birds or their feces. The virus can also be transmitted through contaminated food, water, or equipment.
- Symptoms: PBFD can cause a variety of symptoms, including feather loss, beak deformities, and immunosuppression. Feather loss is the most common symptom and can range from mild to severe. Beak deformities can make it difficult for birds to eat and drink. Immunosuppression can make birds more susceptible to other infections.
- Diagnosis: PBFD is diagnosed based on the bird’s symptoms and a physical exam. A blood test or PCR test can be used to confirm the diagnosis.
- Treatment: There is no cure for PBFD, but treatment can help to manage the symptoms and improve the bird’s quality of life. Treatment may include supportive care, such as providing a nutritious diet and a clean environment, and antiviral medication.
Circoviruses are a major cause of PBFD in psittacine birds. Understanding how circoviruses cause PBFD is essential for developing effective prevention and control strategies.
Symptoms
Feather loss, beak deformities, and immunosuppression are the three main symptoms of psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD). These symptoms can vary in severity, and some birds may only experience one or two of these symptoms. Feather loss is the most common symptom of PBFD, and it can range from mild to severe. In severe cases, birds may lose all of their feathers, which can make it difficult for them to fly and thermoregulate. Beak deformities can also vary in severity, and they can make it difficult for birds to eat and drink. Immunosuppression is another common symptom of PBFD, and it can make birds more susceptible to other infections.
The symptoms of PBFD are caused by the circovirus that causes the disease. The virus attacks the feather follicles and beak, which leads to feather loss and beak deformities. The virus also suppresses the immune system, which makes birds more susceptible to other infections. PBFD is a serious disease that can have a significant impact on the health and well-being of affected birds.
Understanding the connection between the symptoms of PBFD and the disease itself is important for several reasons. First, it helps to diagnose the disease. If a bird is experiencing feather loss, beak deformities, or immunosuppression, it is important to rule out PBFD as a possible cause. Second, understanding the connection between the symptoms of PBFD and the disease itself can help to develop more effective treatments. Finally, understanding the connection between the symptoms of PBFD and the disease itself can help to develop more effective prevention strategies.
Transmission
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is a highly contagious viral disease that affects parrots and other psittacine birds. The virus is shed in the feathers and feces of infected birds, and it can be transmitted to other birds through direct contact or through contact with contaminated food, water, or surfaces.
Understanding the transmission of PBFD is critical for preventing and controlling the disease. Bird owners and breeders should take steps to minimize the risk of their birds coming into contact with infected birds or their feces. This includes quarantining new birds before introducing them to the flock, and disinfecting cages and equipment that may have been contaminated with the virus.
In addition to preventing the spread of PBFD, understanding the transmission of the virus is also important for developing effective treatments. By understanding how the virus is transmitted, researchers can develop targeted therapies that can block the transmission of the virus or prevent it from infecting new cells.
Overall, understanding the transmission of PBFD is essential for preventing, controlling, and treating the disease. Bird owners, breeders, and researchers all have a role to play in preventing the spread of PBFD and protecting the health of psittacine birds.
Diagnosis
An accurate and timely diagnosis is essential for the effective management of psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD). The diagnosis of PBFD is based on a combination of factors, including a physical exam, blood test, and PCR test.
The physical exam can reveal signs of PBFD, such as feather loss, beak deformities, and immunosuppression. The blood test can detect antibodies against the PBFD virus, which indicates that the bird has been exposed to the virus and has developed an immune response. The PCR test can detect the presence of the PBFD virus in the bird’s blood or feathers.
A definitive diagnosis of PBFD can only be made through a PCR test. However, a combination of a physical exam and blood test can provide a strong presumptive diagnosis. It is important to note that some birds may test positive for the PBFD virus but not show any clinical signs of the disease. These birds are considered to be carriers of the virus and can spread it to other birds.
The diagnosis of PBFD is important for several reasons. First, it allows bird owners and breeders to take steps to prevent the spread of the disease to other birds. Second, it allows veterinarians to provide appropriate treatment for the bird. Third, it allows researchers to track the prevalence of the disease and develop new strategies for prevention and control.
Treatment
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is a serious viral disease that affects parrots and other psittacine birds. There is no cure for PBFD, but treatment can help to manage the symptoms and improve the bird’s quality of life. Treatment may include supportive care, such as providing a nutritious diet and a clean environment, and antiviral medication.
- Supportive care: Supportive care is essential for the management of PBFD. This includes providing a nutritious diet, a clean environment, and supportive care, such as hand-feeding and. Supportive care can help to improve the bird’s overall health and well-being, and can help to slow the progression of the disease.
- Antiviral medication: Antiviral medication can be used to treat PBFD. Antiviral medication can help to reduce the amount of virus in the bird’s body and can help to improve the bird’s symptoms. Antiviral medication is typically used in combination with supportive care.
The treatment of PBFD is complex and challenging. However, with proper care, many birds with PBFD can live long and happy lives. It is important to work closely with a veterinarian to develop a treatment plan that is appropriate for the individual bird.
Prevention
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is a highly contagious viral disease that can have a devastating impact on the health and well-being of affected birds. Prevention is essential for controlling the spread of PBFD and protecting psittacine birds.
Vaccination and quarantine of new birds are two of the most important preventive measures that bird owners and breeders can take. Vaccination can help to protect birds from infection with the PBFD virus, and quarantine can help to prevent the spread of the virus from infected birds to healthy birds.
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent PBFD. There are two types of PBFD vaccines available: a live vaccine and an inactivated vaccine. The live vaccine is more effective than the inactivated vaccine, but it can also cause side effects. The inactivated vaccine is less effective than the live vaccine, but it is also less likely to cause side effects.
Quarantine is an important preventive measure for birds that are at risk of exposure to the PBFD virus. Quarantine involves isolating new birds from other birds for a period of time to ensure that they are not infected with the virus. The length of the quarantine period will vary depending on the risk of exposure.
Prevention is essential for controlling the spread of PBFD and protecting psittacine birds. Vaccination and quarantine of new birds are two of the most important preventive measures that bird owners and breeders can take.
Psittacine Beak and Feather Disease FAQs
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is a serious viral disease that affects parrots and other psittacine birds. It is caused by a circovirus, which is a type of virus that has a circular DNA genome. PBFD can cause a variety of symptoms, including feather loss, beak deformities, and immunosuppression. The virus is highly contagious and can be spread through contact with infected birds or their feces. There is no cure for PBFD, but treatment can help to manage the symptoms and improve the bird’s quality of life. Here are some frequently asked questions about PBFD:
Question 1: What are the symptoms of PBFD?
The symptoms of PBFD can vary depending on the individual bird. Some birds may only experience mild symptoms, while others may develop severe symptoms that can be fatal. The most common symptoms of PBFD include feather loss, beak deformities, and immunosuppression. Feather loss is the most common symptom, and it can range from mild to severe. Beak deformities can make it difficult for birds to eat and drink. Immunosuppression can make birds more susceptible to other infections.
Question 2: How is PBFD diagnosed?
PBFD is diagnosed based on the bird’s symptoms and a physical exam. A blood test or PCR test can be used to confirm the diagnosis. A blood test can detect antibodies against the PBFD virus, which indicates that the bird has been exposed to the virus and has developed an immune response. A PCR test can detect the presence of the PBFD virus in the bird’s blood or feathers.
Question 3: Is there a cure for PBFD?
There is no cure for PBFD. Treatment can help to manage the symptoms and improve the bird’s quality of life, but it cannot cure the disease. Treatment may include supportive care, such as providing a nutritious diet and a clean environment, and antiviral medication.
Question 4: How can I prevent my bird from getting PBFD?
There are several things you can do to prevent your bird from getting PBFD. Vaccination and quarantine of new birds are two of the most important preventive measures. Vaccination can help to protect your bird from infection with the PBFD virus, and quarantine can help to prevent the spread of the virus from infected birds to healthy birds.
Question 5: What should I do if my bird has PBFD?
If your bird has PBFD, it is important to seek veterinary care as soon as possible. Treatment can help to manage the symptoms and improve your bird’s quality of life. Treatment may include supportive care, such as providing a nutritious diet and a clean environment, and antiviral medication.
Question 6: Is PBFD contagious to humans?
PBFD is not contagious to humans. It is a virus that only affects birds.
PBFD is a serious disease, but it can be managed with proper care. If you have any questions about PBFD, please consult with your veterinarian.
Next Article Section: Conclusion
Tips to Prevent and Control Psittacine Beak and Feather Disease
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is a serious viral disease that affects parrots and other psittacine birds. It is caused by a circovirus, which is a type of virus that has a circular DNA genome. PBFD can cause a variety of symptoms, including feather loss, beak deformities, and immunosuppression. The virus is highly contagious and can be spread through contact with infected birds or their feces. There is no cure for PBFD, but treatment can help to manage the symptoms and improve the bird’s quality of life.
Here are five tips to help prevent and control PBFD:
Tip 1: Vaccinate your birds.
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent PBFD. There are two types of PBFD vaccines available: a live vaccine and an inactivated vaccine. The live vaccine is more effective than the inactivated vaccine, but it can also cause side effects. The inactivated vaccine is less effective than the live vaccine, but it is also less likely to cause side effects. Talk to your veterinarian about which vaccine is right for your bird.
Tip 2: Quarantine new birds.
Quarantine new birds for at least 30 days before introducing them to your flock. This will help to prevent the spread of PBFD and other diseases. During quarantine, keep the new bird in a separate cage in a different room from your other birds. Monitor the new bird for any signs of illness.
Tip 3: Practice good hygiene.
Keep your bird’s cage and environment clean to help prevent the spread of PBFD. Wash your hands before and after handling your bird, and disinfect your bird’s cage and toys regularly. Avoid contact with wild birds, as they may be carrying the PBFD virus.
Tip 4: Isolate sick birds.
If you think your bird may be sick, isolate it from your other birds immediately. Contact your veterinarian as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to improve your bird’s chances of survival.
Tip 5: Educate yourself about PBFD.
The more you know about PBFD, the better you can protect your birds from this devastating disease. Talk to your veterinarian, read books and articles about PBFD, and stay up-to-date on the latest research.
By following these tips, you can help to prevent and control PBFD and protect the health of your psittacine birds.
Conclusion
PBFD is a serious disease, but it can be managed with proper care. By taking steps to prevent and control PBFD, you can help to protect the health of your birds and ensure that they live long, happy lives.
Conclusion
Psittacine beak and feather disease (PBFD) is a serious viral disease that can have a devastating impact on parrots and other psittacine birds. There is no cure for PBFD, but early diagnosis and treatment can help to improve the bird’s quality of life and chances of survival. Bird owners and breeders should take steps to prevent the spread of PBFD, including vaccination, quarantine of new birds, and good hygiene practices.
By working together, we can help to protect psittacine birds from this devastating disease.
Youtube Video: